Quantum Threat to Cryptocurrencies: Blockchains Prepare for "Q-Day" as Early as 2026
According to the latest estimates, "Q-Day", the day when quantum technologies can break traditional cryptography - may arrive as early as 2030. Circle, one of the leading stablecoin issuers, emphasizes in its blog that the quantum threat is closer than it seems and calls for immediate migration to post-quantum protection. This applies not only to Bitcoin and Ethereum but to the entire ecosystem, including institutional wallets and ZK-systems.
Vulnerabilities of Modern Cryptography
Quantum computers, using Shor's algorithm, can break cryptography based on elliptic curves (such as ECDSA and Ed25519) and RSA. This puts signatures in Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other networks at risk. Hash functions like SHA-256 and symmetric encryption AES are still resistant, but elliptic curves are not. U.S. and EU regulators require the transition of critical infrastructure to post-quantum algorithms by 2030.
Estimates suggest that migrating all UTXO (unspent transaction outputs) in the Bitcoin network would take about 76 days of continuous processing. Active addresses where the public key has already been revealed will need to be fully replaced with post-quantum ones. Passive Ed25519 addresses can be recovered after "Q-Day" by proving knowledge of the seed, and ECDSA addresses from BIP-32/BIP-39 similarly.
Risks for Institutional Investors
Institutional wallets using multi-party computation (MPC) and threshold signatures based on elliptic curves are particularly vulnerable. Such schemes cannot simply be updated, the entire cryptography will need to be replaced. Blockchain-specific HSMs (hardware security modules) are not yet available, but post-quantum HSMs and cloud services from AWS and Google are emerging.
In 2025-2026, experts predict significant progress in hardware acceleration, algorithm optimization, and implementation efficiency of post-quantum cryptography. The U.S. Federal Reserve report warns that quantum computers could decrypt historical Bitcoin transactions. Conferences such as Post-Quantum Blockchain Day 2025 and Post-Quantum Cryptography Conference 2025emphasize the need for global migration.
Internet Transition and Changes in Signatures
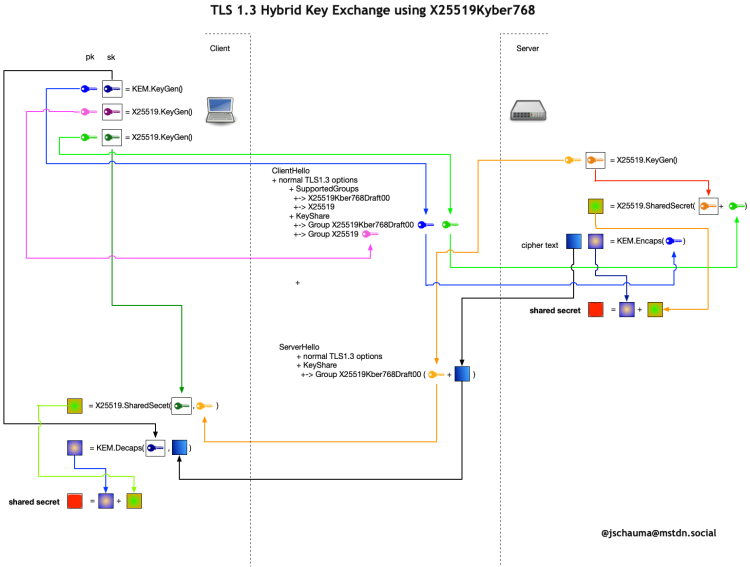
The internet is already adapting: TLS 1.3 supports post-quantum algorithms, and Google and AWS are moving to hybrid schemes like X25519 + ML-KEM. NIST has approved ML-KEM, and the hybrid X25519MLKEM768 has become an industry standard. In 2024, NIST released three post-quantum cryptography standards, and organizations are already migrating systems. By 2026, the first wave of mandatory PQC compliance requirements is expected.
Signatures will also change: 65-byte ECDSA will be replaced by larger ones, ML-DSA (2420 bytes), Falcon (666 bytes, considered for Ethereum), or SLH-DSA-SHA2-128s (7856 bytes, proposed for Aptos). Optimizations include ML-DSA with BLAKE3, and XMSS is suitable for validators but not for transactions.
Impact on ZK-Systems and New Projects
ZK-systems like Groth16, Halo2, and Plonk are vulnerable due to elliptic curves. The future lies with quantum-resistant alternatives: STARK, SNARG, FRI, STIR, and WHIR. They are more expensive and slower but resilient. Starknet is transitioning to FRI, and Ethereum is considering FRI, STIR, and WHIR.
In the X community, the threat is actively discussed. The OP_NET project has already implemented MLDSA for quantum protection on testnet. QANplatform positions itself as a quantum-protection solution.
Mochimo has been resistant since 2018. QRL showed a 100% price increase recently, with a market capitalization of $195 million. Experts from CoinMarketCap consider the threat to Bitcoin in 2026 theoretical but advise not reusing addresses and monitoring updates.
Experts recommend publishing specifications and roadmaps immediately, considering HSM compatibility, and using smart contract wallets for custom signatures. The CERN report on quantum diplomacy for 2025-2026 highlights the acceleration of quantum technology development. Projects like Abelian, QRL, and others are worth attention in 2026.
The quantum threat is not a hypothesis but a real planning issue. The crypto industry must build crypto-agility now to avoid chaos. With the transition to post-quantum standards like lattice-based cryptography (selected by NIST), the future of blockchains can be secure.

3 free cases and a 5% bonus added to all cash deposits.
5 Free Cases, Daily FREE & Welcome Bonuses up to 35%

a free Gift Case


EGAMERSW - get 11% Deposit Bonus + Bonus Wheel free spin
EXTRA 10% DEPOSIT BONUS + free 2 spins
3 Free Cases + 100% up to 100 Coins on First Deposit


Comments